注意
点击 这里 下载完整示例代码
2. 在 MS COCO 上端到端训练 Mask RCNN¶
本教程将引导您完成训练由 GluonCV 提供的 Mask R-CNN [He17] 实例分割模型的步骤。
Mask R-CNN 是 Faster R-CNN [Ren15] 目标检测模型的扩展。因此,本教程也是 06. 在 PASCAL VOC 上端到端训练 Faster-RCNN 的扩展。我们将重点介绍在 Faster R-CNN 基础上额外的工作,展示如何使用 GluonCV 组件构建 Mask R-CNN 模型。
强烈建议阅读原始论文 [Girshick14]、[Girshick15]、[Ren15]、[He17] 以了解 Mask R-CNN 背后的更多思想。[He16] 的附录和 [Lin17] 的实验细节也可能是很有用的参考。
提示
请先阅读此 准备 COCO 数据集 教程,以便在您的磁盘上设置 MSCOCO 数据集。
提示
您可以跳过本教程的其余部分,通过下载此脚本立即开始训练您的 Mask RCNN 模型
示例用法
在 GPU 0 上使用 COCO 数据集训练默认的 resnet50_v1b 模型
python train_mask_rcnn.py --gpus 0
在 GPU 0,1,2,3 上训练
python train_mask_rcnn.py --gpus 0,1,2,3
检查支持的参数
python train_mask_rcnn.py --help
数据集¶
确保 COCO 数据集已在您的磁盘上设置好。然后,我们就可以加载训练和验证图像了。
from gluoncv.data import COCOInstance
# typically we use train2017 (i.e. train2014 + minival35k) split as training data
# COCO dataset actually has images without any objects annotated,
# which must be skipped during training to prevent empty labels
train_dataset = COCOInstance(splits='instances_train2017', skip_empty=True)
# and val2014 (i.e. minival5k) test as validation data
val_dataset = COCOInstance(splits='instances_val2017', skip_empty=False)
print('Training images:', len(train_dataset))
print('Validation images:', len(val_dataset))
输出
loading annotations into memory...
Done (t=13.42s)
creating index...
index created!
loading annotations into memory...
Done (t=0.38s)
creating index...
index created!
Training images: 117266
Validation images: 5000
数据转换¶
我们可以从训练数据集中读取一个 (image, label, segm) 元组
train_image, train_label, train_segm = train_dataset[6]
bboxes = train_label[:, :4]
cids = train_label[:, 4:5]
print('image:', train_image.shape)
print('bboxes:', bboxes.shape, 'class ids:', cids.shape)
# segm is a list of polygons which are arrays of points on the object boundary
print('masks', [[poly.shape for poly in polys] for polys in train_segm])
输出
image: (500, 381, 3)
bboxes: (9, 4) class ids: (9, 1)
masks [[(95, 2)], [(32, 2)], [(31, 2)], [(50, 2)], [(54, 2)], [(13, 2)], [(24, 2)], [(10, 2), (15, 2)], [(21, 2)]]
绘制带有框和标签的图像
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from gluoncv.utils import viz
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax = viz.plot_bbox(train_image, bboxes, labels=cids, class_names=train_dataset.classes, ax=ax)
plt.show()

要实际查看对象分割结果,我们需要将多边形转换为掩码
import numpy as np
from gluoncv.data.transforms import mask as tmask
width, height = train_image.shape[1], train_image.shape[0]
train_masks = np.stack([tmask.to_mask(polys, (width, height)) for polys in train_segm])
plt_image = viz.plot_mask(train_image, train_masks)
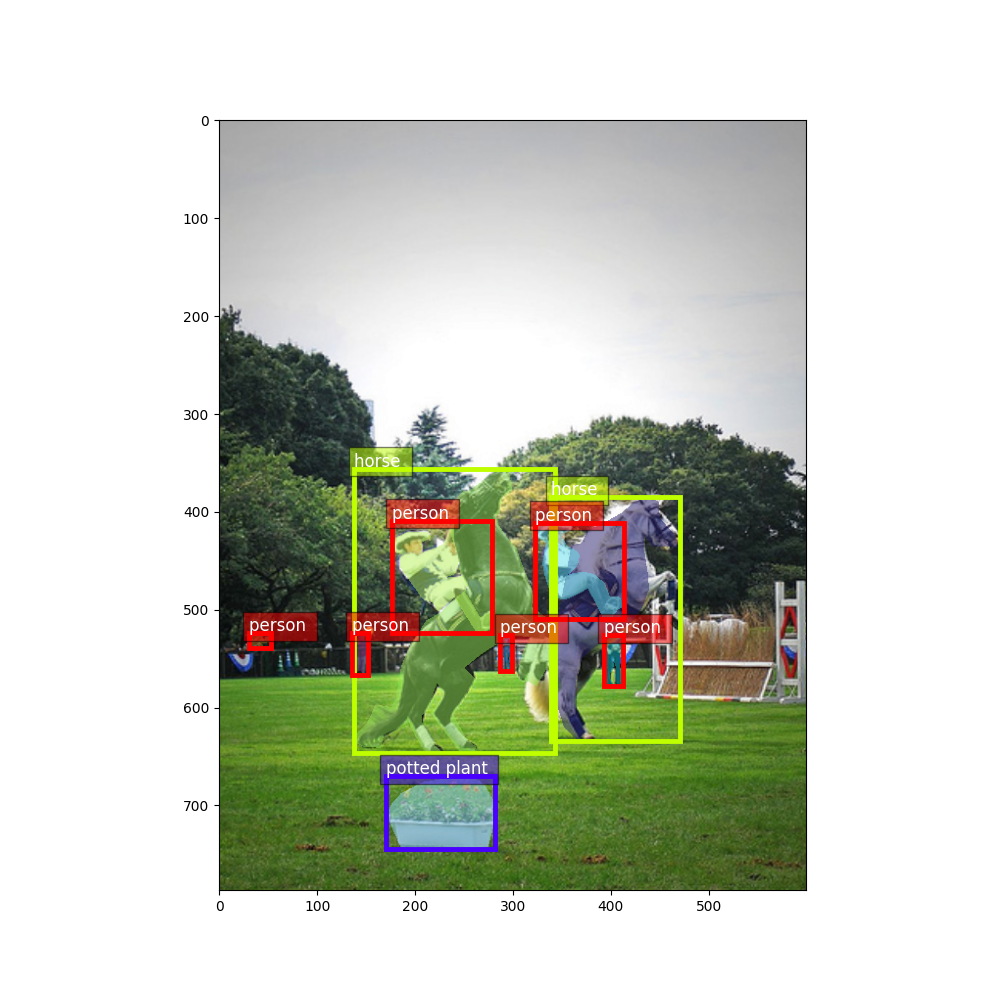
现在绘制带有框、标签和掩码的图像
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax = viz.plot_bbox(plt_image, bboxes, labels=cids, class_names=train_dataset.classes, ax=ax)
plt.show()

数据转换,即解码和变换,与 Faster R-CNN 相同,但额外增加了分割多边形输入。gluoncv.data.transforms.presets.rcnn.MaskRCNNDefaultTrainTransform 将分割多边形转换为二进制分割掩码。gluoncv.data.transforms.presets.rcnn.MaskRCNNDefaultValTransform 忽略分割多边形,返回图像张量和 [im_height, im_width, im_scale]。
from gluoncv.data.transforms import presets
from gluoncv import utils
from mxnet import nd
short, max_size = 600, 1000 # resize image to short side 600 px, but keep maximum length within 1000
train_transform = presets.rcnn.MaskRCNNDefaultTrainTransform(short, max_size)
val_transform = presets.rcnn.MaskRCNNDefaultValTransform(short, max_size)
utils.random.seed(233) # fix seed in this tutorial
将转换应用于训练图像
train_image2, train_label2, train_masks2 = train_transform(train_image, train_label, train_segm)
print('tensor shape:', train_image2.shape)
print('box and id shape:', train_label2.shape)
print('mask shape', train_masks2.shape)
输出
tensor shape: (3, 787, 600)
box and id shape: (9, 5)
mask shape (9, 787, 600)
张量中的图像由于不再位于 (0, 255) 范围内而失真。让我们将它们转换回去,以便清楚地看到它们。
plt_image2 = train_image2.transpose((1, 2, 0)) * nd.array((0.229, 0.224, 0.225)) + nd.array(
(0.485, 0.456, 0.406))
plt_image2 = (plt_image2 * 255).asnumpy().astype('uint8')
转换已经将多边形转换为掩码,我们可以直接绘制它们。
width, height = plt_image2.shape[1], plt_image2.shape[0]
plt_image2 = viz.plot_mask(plt_image2, train_masks2)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax = viz.plot_bbox(plt_image2, train_label2[:, :4],
labels=train_label2[:, 4:5],
class_names=train_dataset.classes,
ax=ax)
plt.show()
数据加载器¶
数据加载器与 Faster R-CNN 相同,区别在于掩码输入和输出。
from gluoncv.data.batchify import Tuple, Append, MaskRCNNTrainBatchify
from mxnet.gluon.data import DataLoader
batch_size = 2 # for tutorial, we use smaller batch-size
num_workers = 0 # you can make it larger(if your CPU has more cores) to accelerate data loading
train_bfn = Tuple(*[Append() for _ in range(3)])
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset.transform(train_transform), batch_size, shuffle=True,
batchify_fn=train_bfn, last_batch='rollover', num_workers=num_workers)
val_bfn = Tuple(*[Append() for _ in range(2)])
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset.transform(val_transform), batch_size, shuffle=False,
batchify_fn=val_bfn, last_batch='keep', num_workers=num_workers)
for ib, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
if ib > 3:
break
print('data 0:', batch[0][0].shape, 'label 0:', batch[1][0].shape, 'mask 0:', batch[2][0].shape)
print('data 1:', batch[0][1].shape, 'label 1:', batch[1][1].shape, 'mask 1:', batch[2][1].shape)
输出
data 0: (1, 3, 600, 901) label 0: (1, 2, 5) mask 0: (1, 2, 600, 901)
data 1: (1, 3, 800, 600) label 1: (1, 1, 5) mask 1: (1, 1, 800, 600)
data 0: (1, 3, 798, 600) label 0: (1, 2, 5) mask 0: (1, 2, 798, 600)
data 1: (1, 3, 600, 600) label 1: (1, 18, 5) mask 1: (1, 18, 600, 600)
data 0: (1, 3, 600, 800) label 0: (1, 1, 5) mask 0: (1, 1, 600, 800)
data 1: (1, 3, 600, 600) label 1: (1, 5, 5) mask 1: (1, 5, 600, 600)
data 0: (1, 3, 600, 800) label 0: (1, 2, 5) mask 0: (1, 2, 600, 800)
data 1: (1, 3, 800, 600) label 1: (1, 21, 5) mask 1: (1, 21, 800, 600)
Mask RCNN 网络¶
在 GluonCV 中,Mask RCNN 网络 gluoncv.model_zoo.MaskRCNN 继承自 Faster RCNN 网络 gluoncv.model_zoo.FasterRCNN。
Gluon 模型库 中有一些 Mask RCNN 预训练网络。您只需一行简单的代码即可加载您喜欢的网络
提示
为避免在本教程中下载模型,我们将 pretrained_base=False,但在实际应用中,通常希望通过设置 pretrained_base=True 来加载预训练的 ImageNet 模型。
from gluoncv import model_zoo
net = model_zoo.get_model('mask_rcnn_resnet50_v1b_coco', pretrained_base=False)
print(net)
输出
MaskRCNN(
(features): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(None -> 64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), padding=(3, 3), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=64)
(2): Activation(relu)
(3): MaxPool2D(size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), ceil_mode=False, global_pool=False, pool_type=max, layout=NCHW)
(4): HybridSequential(
(0): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=64)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=64)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
)
)
(1): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=64)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=64)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(2): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 64, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=64)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=64)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
)
(5): HybridSequential(
(0): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
)
)
(1): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(2): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(3): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=128)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
)
(6): HybridSequential(
(0): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=1024)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=1024)
)
)
(1): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=1024)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(2): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=1024)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(3): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=1024)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(4): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=1024)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(5): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=256)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=1024)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
)
)
(top_features): HybridSequential(
(0): HybridSequential(
(0): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=2048)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
(downsample): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(None -> 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(2, 2), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=2048)
)
)
(1): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=2048)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
(2): BottleneckV1b(
(conv1): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu1): Activation(relu)
(conv2): Conv2D(None -> 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=512)
(relu2): Activation(relu)
(conv3): Conv2D(None -> 2048, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm(axis=1, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, fix_gamma=False, use_global_stats=True, in_channels=2048)
(relu3): Activation(relu)
)
)
)
(class_predictor): Dense(None -> 81, linear)
(box_predictor): Dense(None -> 320, linear)
(cls_decoder): MultiPerClassDecoder(
)
(box_decoder): NormalizedBoxCenterDecoder(
(corner_to_center): BBoxCornerToCenter(
)
)
(rpn): RPN(
(anchor_generator): RPNAnchorGenerator(
)
(conv1): HybridSequential(
(0): Conv2D(None -> 1024, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): Activation(relu)
)
(score): Conv2D(None -> 15, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(loc): Conv2D(None -> 60, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(region_proposer): RPNProposal(
(_box_to_center): BBoxCornerToCenter(
)
(_box_decoder): NormalizedBoxCenterDecoder(
(corner_to_center): BBoxCornerToCenter(
)
)
(_clipper): BBoxClipToImage(
)
)
)
(sampler): RCNNTargetSampler(
)
(mask): Mask(
(deconv): Conv2DTranspose(256 -> 0, kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=(2, 2))
(mask): Conv2D(None -> 80, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(mask_target): MaskTargetGenerator(
)
)
Mask-RCNN 的输入相同,但会额外生成一个输出。cids 是类别标签,scores 是每个预测的置信度分数,bboxes 是相应边界框的绝对坐标。masks 是与每个边界框对应的预测分割掩码。
训练期间,会返回一个额外输出:mask_preds 是除 cls_preds、box_preds 之外的每个类别的掩码预测。
from mxnet import autograd
with autograd.train_mode():
# this time we need ground-truth to generate high quality roi proposals during training
gt_box = mx.nd.zeros(shape=(1, 1, 4))
gt_label = mx.nd.zeros(shape=(1, 1, 1))
cls_pred, box_pred, mask_pred, roi, samples, matches, rpn_score, rpn_box, anchors, \
cls_targets, box_targets, box_masks, indices = net(x, gt_box, gt_label)
训练损失¶
Mask-RCNN 中有一个额外的损失函数。
# the loss to penalize incorrect foreground/background prediction
rpn_cls_loss = mx.gluon.loss.SigmoidBinaryCrossEntropyLoss(from_sigmoid=False)
# the loss to penalize inaccurate anchor boxes
rpn_box_loss = mx.gluon.loss.HuberLoss(rho=1 / 9.) # == smoothl1
# the loss to penalize incorrect classification prediction.
rcnn_cls_loss = mx.gluon.loss.SoftmaxCrossEntropyLoss()
# and finally the loss to penalize inaccurate proposals
rcnn_box_loss = mx.gluon.loss.HuberLoss() # == smoothl1
# the loss to penalize incorrect segmentation pixel prediction
rcnn_mask_loss = mx.gluon.loss.SigmoidBinaryCrossEntropyLoss(from_sigmoid=False)
训练目标¶
RPN 和 RCNN 训练目标与 06. 在 PASCAL VOC 上端到端训练 Faster-RCNN 中相同。
我们还将 RPN 目标的计算推送到 CPU worker,因此网络会传递给转换函数
train_transform = presets.rcnn.MaskRCNNDefaultTrainTransform(short, max_size, net)
# return images, labels, masks, rpn_cls_targets, rpn_box_targets, rpn_box_masks loosely
batchify_fn = MaskRCNNTrainBatchify(net)
# For the next part, we only use batch size 1
batch_size = 1
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset.transform(train_transform), batch_size, shuffle=True,
batchify_fn=batchify_fn, last_batch='rollover', num_workers=num_workers)
掩码目标是在生成 RCNN 目标后的中间输出中生成的。
for ib, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
if ib > 0:
break
with autograd.train_mode():
for data, label, masks, rpn_cls_targets, rpn_box_targets, rpn_box_masks in zip(*batch):
label = label.expand_dims(0)
gt_label = label[:, :, 4:5]
gt_box = label[:, :, :4]
# network forward
cls_pred, box_pred, mask_pred, roi, samples, matches, rpn_score, rpn_box, anchors, \
cls_targets, box_targets, box_masks, indices = \
net(data.expand_dims(0), gt_box, gt_label)
# generate targets for mask head
roi = mx.nd.concat(
*[mx.nd.take(roi[i], indices[i]) for i in range(indices.shape[0])], dim=0) \
.reshape((indices.shape[0], -1, 4))
m_cls_targets = mx.nd.concat(
*[mx.nd.take(cls_targets[i], indices[i]) for i in range(indices.shape[0])], dim=0) \
.reshape((indices.shape[0], -1))
matches = mx.nd.concat(
*[mx.nd.take(matches[i], indices[i]) for i in range(indices.shape[0])], dim=0) \
.reshape((indices.shape[0], -1))
mask_targets, mask_masks = net.mask_target(roi, masks.expand_dims(0), matches,
m_cls_targets)
print('data:', data.shape)
# box and class labels
print('box:', gt_box.shape)
print('label:', gt_label.shape)
# -1 marks ignored label
print('rpn cls label:', rpn_cls_targets.shape)
# mask out ignored box label
print('rpn box label:', rpn_box_targets.shape)
print('rpn box mask:', rpn_box_masks.shape)
# rcnn does not have ignored label
print('rcnn cls label:', cls_targets.shape)
# mask out ignored box label
print('rcnn box label:', box_targets.shape)
print('rcnn box mask:', box_masks.shape)
print('rcnn mask label:', mask_targets.shape)
print('rcnn mask mask:', mask_masks.shape)
输出
data: (3, 831, 600)
box: (1, 1, 4)
label: (1, 1, 1)
rpn cls label: (1, 29640)
rpn box label: (1, 29640, 4)
rpn box mask: (1, 29640, 4)
rcnn cls label: (1, 128)
rcnn box label: (1, 32, 80, 4)
rcnn box mask: (1, 32, 80, 4)
rcnn mask label: (1, 32, 80, 14, 14)
rcnn mask mask: (1, 32, 80, 14, 14)
训练循环¶
定义了损失函数并生成训练目标后,我们就可以编写训练循环了。
for ib, batch in enumerate(train_loader):
if ib > 0:
break
with autograd.record():
for data, label, masks, rpn_cls_targets, rpn_box_targets, rpn_box_masks in zip(*batch):
label = label.expand_dims(0)
gt_label = label[:, :, 4:5]
gt_box = label[:, :, :4]
# network forward
cls_preds, box_preds, mask_preds, roi, samples, matches, rpn_score, rpn_box, anchors, \
cls_targets, box_targets, box_masks, indices = \
net(data.expand_dims(0), gt_box, gt_label)
# generate targets for mask head
roi = mx.nd.concat(
*[mx.nd.take(roi[i], indices[i]) for i in range(indices.shape[0])], dim=0) \
.reshape((indices.shape[0], -1, 4))
m_cls_targets = mx.nd.concat(
*[mx.nd.take(cls_targets[i], indices[i]) for i in range(indices.shape[0])], dim=0) \
.reshape((indices.shape[0], -1))
matches = mx.nd.concat(
*[mx.nd.take(matches[i], indices[i]) for i in range(indices.shape[0])], dim=0) \
.reshape((indices.shape[0], -1))
mask_targets, mask_masks = net.mask_target(roi, masks.expand_dims(0), matches,
m_cls_targets)
# losses of rpn
rpn_score = rpn_score.squeeze(axis=-1)
num_rpn_pos = (rpn_cls_targets >= 0).sum()
rpn_loss1 = rpn_cls_loss(rpn_score, rpn_cls_targets,
rpn_cls_targets >= 0) * rpn_cls_targets.size / num_rpn_pos
rpn_loss2 = rpn_box_loss(rpn_box, rpn_box_targets,
rpn_box_masks) * rpn_box.size / num_rpn_pos
# losses of rcnn
num_rcnn_pos = (cls_targets >= 0).sum()
rcnn_loss1 = rcnn_cls_loss(cls_preds, cls_targets,
cls_targets >= 0) * cls_targets.size / cls_targets.shape[
0] / num_rcnn_pos
rcnn_loss2 = rcnn_box_loss(box_preds, box_targets, box_masks) * box_preds.size / \
box_preds.shape[0] / num_rcnn_pos
# loss of mask
mask_loss = rcnn_mask_loss(mask_preds, mask_targets, mask_masks) * mask_targets.size / \
mask_targets.shape[0] / mask_masks.sum()
# some standard gluon training steps:
# autograd.backward([rpn_loss1, rpn_loss2, rcnn_loss1, rcnn_loss2, mask_loss])
# trainer.step(batch_size)
提示
请查看完整的 训练脚本 以获取完整的实现。
参考文献¶
- Girshick14
Ross Girshick、Jeff Donahue、Trevor Darrell 和 Jitendra Malik。用于准确目标检测和语义分割的丰富特征层级。CVPR 2014。
- Girshick15
Ross Girshick。Fast {R-CNN}。ICCV 2015。
- Ren15(1,2)
邵卿、何恺明、Ross Girshick 和 孙剑。Faster {R-CNN}:利用区域提议网络实现实时目标检测。NIPS 2015。
- He16
何恺明、张向雨、邵卿 和 孙剑。用于图像识别的深度残差学习。CVPR 2016。
- Lin17
林宗一、Piotr Dollár、Ross Girshick、何恺明、Bharath Hariharan 和 Serge Belongie。用于目标检测的特征金字塔网络。CVPR 2017。
- He17(1,2)
何恺明、Georgia Gkioxari、Piotr Dollár 和 Ross Girshick。Mask {R-CNN}。ICCV 2017。
脚本总运行时间:( 6 分 6.824 秒)